FAQ
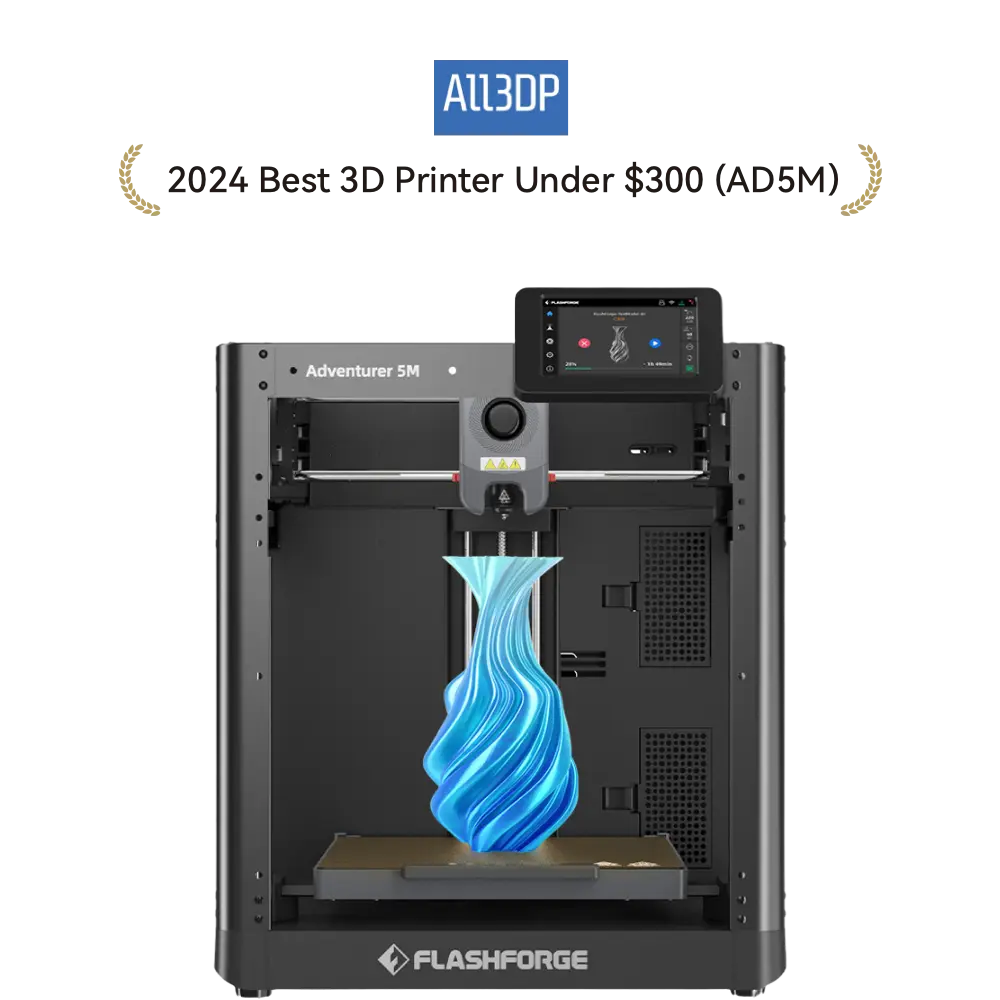
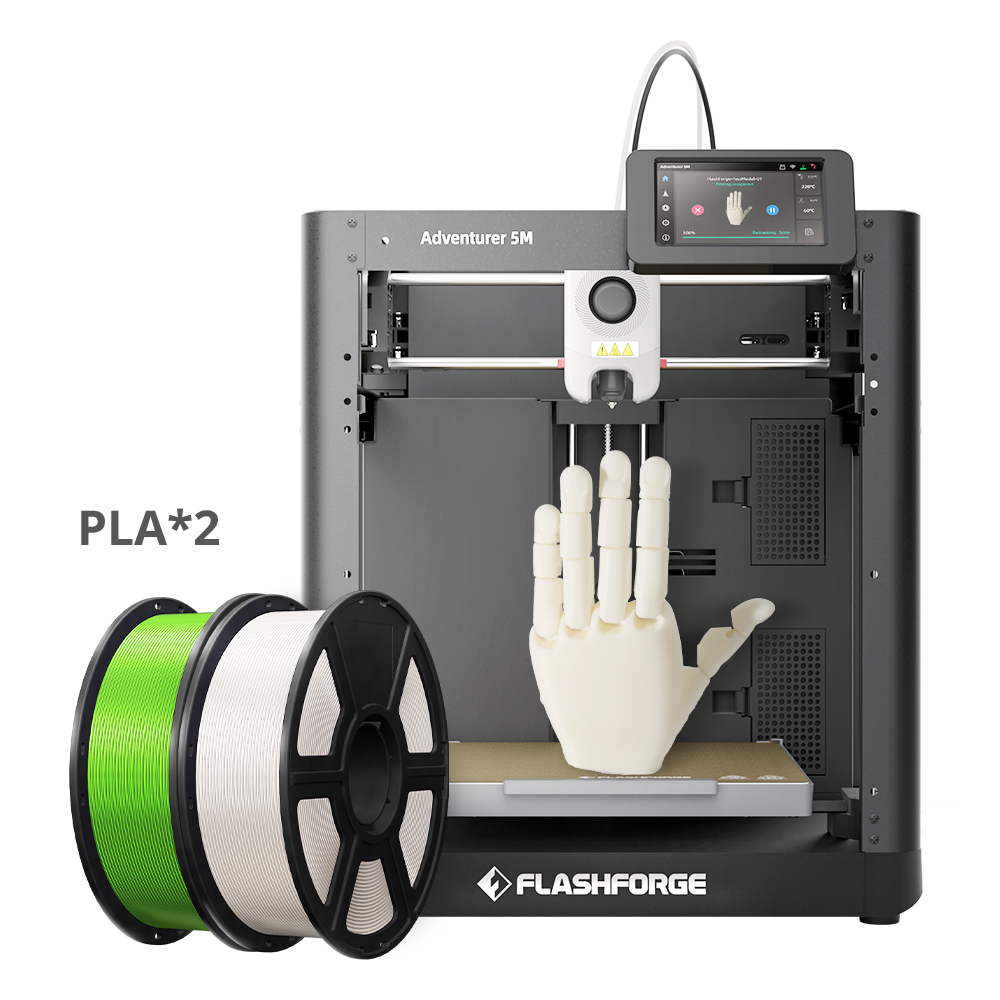
The Adventurer 5M offers the best value for beginners. It’s easy to set up in under 10 minutes, requires no experience, and delivers fast, high-quality prints. Key features include:
- 220 × 220 × 220 mm build volume – great for most projects
- 600mm/s max speed & 20000mm/s² acceleration – prints fast without losing quality
- CoXY all-metal structure – minimizes errors from vibrations
- Quick-detach nozzles – easy maintenance for smooth printing
Start your 3D printing journey hassle-free with the Adventurer 5M!
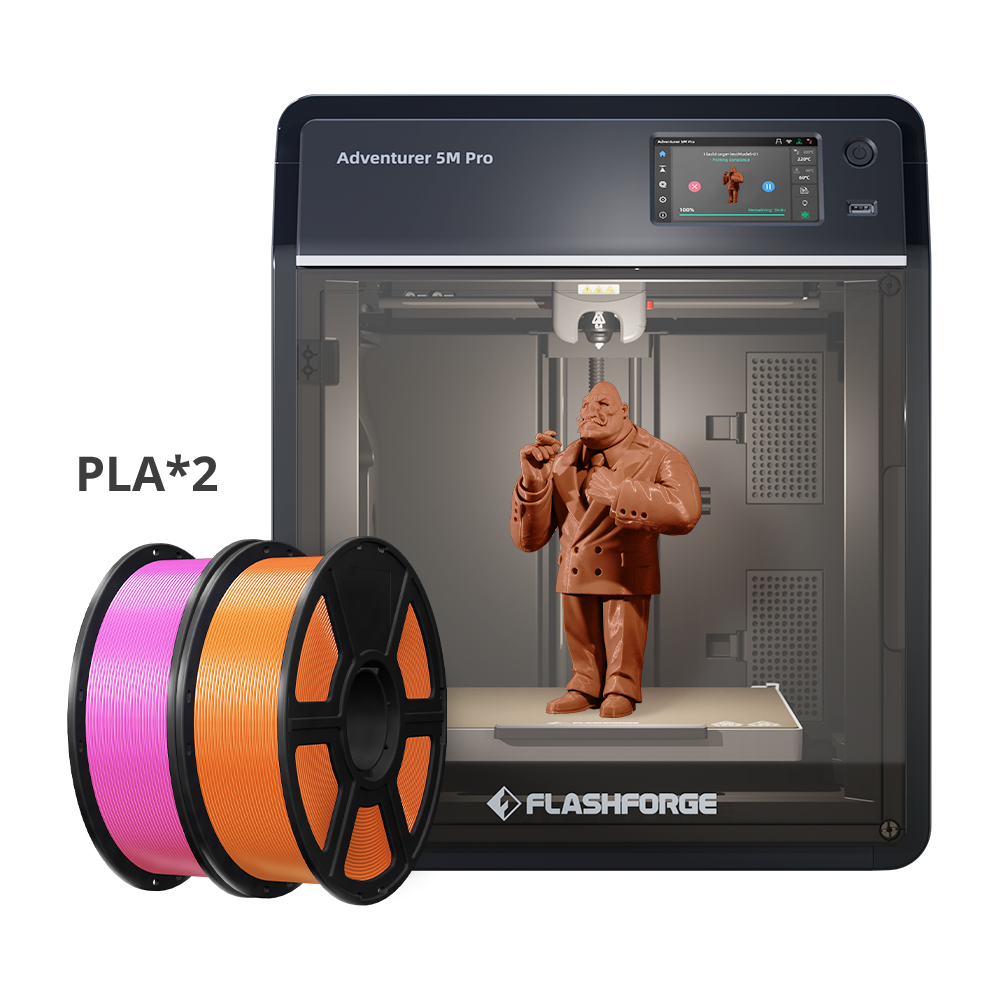
The AD5M is a great choice for beginners, offering an easy and affordable start to 3D printing. The 5M Pro is an upgraded version with a fully enclosed design, built-in camera, and air filter, providing a better printing experience.
- Adventurer 5M – Best for beginners, open-frame design
- Adventurer 5M Pro – Enclosed for safety, ideal for offices, schools, and studios
If you need a more professional setup with extra features, the 5M Pro is the way to go!
The G3U offers the largest build volume at 330 × 330 × 600 mm, making it ideal for large-scale projects. Key features include:
- 500mm/s printing speed – fast and efficient
- Hands-free auto bed leveling & calibration – hassle-free setup
- Core-XY structure – ensures stability and precision
- Dual extruders – perfect for complex models with soluble supports
- 1-year warranty on the printer, 3 months on extruder parts
If you need a high-speed, large-format 3D printer, the G3U is the top choice!
3D printing is a manufacturing process that transforms digital models into physical objects by building them layer by layer. This allows for the creation of complex designs, from prototypes to functional parts and finished products.
At Flashforge, we specialize in FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printers, known for their reliability, affordability, and ease of use—perfect for beginners and professionals alike.
3D printing technology has wide-ranging applications across various industries, including industrial manufacturing, healthcare, architecture, automotive, and aerospace. It can be used for rapid prototyping, custom product creation, medical devices, and spare parts manufacturing, among others.
Choosing the right 3D printer for your needs depends on several factors, such as printing materials, printing speed, printing accuracy, and print size. Common types include FFF/FDM printers, SLA/DLP printers, and SLS printers, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages.
Proper maintenance and care of a 3D printer are essential to ensure its long-term reliability. Common maintenance tasks include cleaning the print head, calibrating the print bed, and replacing consumables. Regular inspections and maintenance can prolong the life of the equipment and ensure print quality.